Medical Weight Loss Program in Shoreline, WA
Obesity is a serious health issue that raises the risk of chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and joint problems. A weight loss program helps by offering a structured approach that combines diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. With personalized plans designed to meet individual needs, these programs promote long-term success, enhance overall health, and reduce the risk of complications related to obesity. For more information, contact us or request an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 1507 NE 150th St, Suite A, Shoreline, WA 98155.

Global Statistics
Obesity is a global crisis affecting over 650 million adults and 20% of children worldwide, with more than 40% of U.S. adults classified as obese. It results from a combination of genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors, leading to excessive caloric intake, reduced energy expenditure, and hormonal imbalances.
Chemistry
Obesity is associated with a chemical imbalance involving hormones that regulate hunger and satiety.
In individuals with obesity, hormone resistance can develop, leading to persistent hunger.
Additionally, insulin resistance occurs, causing the body to struggle with regulating blood sugar and fat storage, further contributing to weight gain.
Complications
Risk of serious health complications including: type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
It can also lead to conditions like high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and fatty liver disease.
Obesity is also associated with certain cancers, reduced mobility, and a lower quality of life
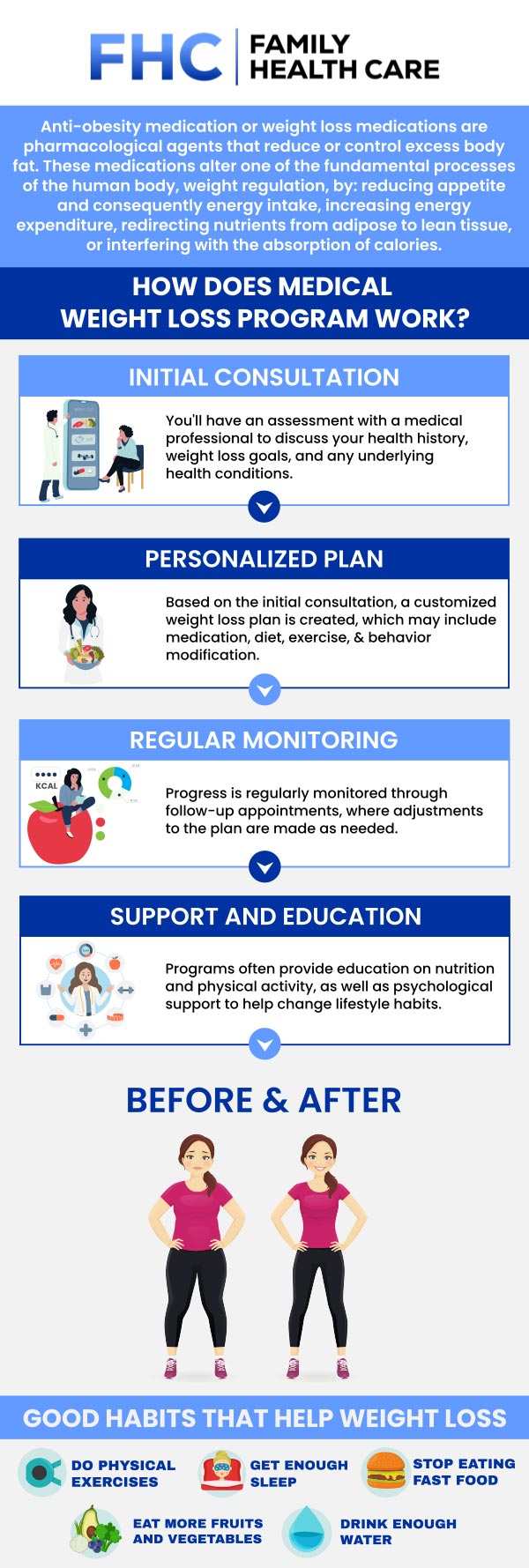
Modern Treatment
• In addition to lifestyle changes, GLP-1 agonists are a class of medications that help treat obesity
• They mimic the action of the hormone that regulates appetite and sugar metabolism
• These drugs reduce hunger and increase feelings of fullness, leading to reduced food intake and weight loss
• GLP-1 agonists, like semaglutide (Ozempic) or tirzepatide (Mounjarno or Zepbound), have shown significant success in helping patients achieve sustained weight loss alongside lifestyle changes
To learn more, schedule a consultation
Weight Loss Program Cancellation Policy
At Family Health Care, we are committed to providing our clients with the highest quality of care and support throughout their weight loss journey. To ensure the best possible service, we have implemented the following cancellation policy:
1. Appointment Cancellations
We kindly ask that you provide at least 24 hours’ notice if you need to cancel or reschedule your appointment.
Cancellations made with less than 24 hours’ notice may incur a $49 cancellation fee.
2. No-Show Policy
Clients who fail to attend a scheduled appointment without prior notification will be considered a “no-show.”
Refunds are not available for “no-show”; however, they may be rescheduled if the cancellation policy is adhered to.
3. Prepaid Packages and Programs
If you are unable to attend a session within a prepaid weight loss package, the session will be forfeited unless a minimum of 24 hours’ notice is provided.
Refunds are not available for unused sessions in prepaid programs; however, they may be rescheduled if the cancellation policy is adhered to.
4. Late Arrivals
If you arrive more than 15 minutes late, we may need to reschedule your appointment to ensure that our schedule runs smoothly.
5. Emergency Cancellations
We understand that emergencies happen. If you need to cancel due to an emergency, please contact our office as soon as possible, and we will do our best to accommodate the situation on a case-by-case basis.
6. How to Cancel
To cancel or reschedule your appointment, please call our office or visit our website.
Cancellations via text or direct message through social media platforms will not be accepted.
Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Need
• Weight Loss Management
• Diabetes
• Hypertension
• Geriatric
• Personalized Care
• Primary Care
• Musculoskeletal Injuries
• Preventative Care
• Mental Health
• Heart Disease
• Congestive Heart Failure
• Same Day Sick Visits
• Physical Exams
• Chronic Care Management
• Wellness Visits
• Vitamin B12 Injections
• Oral GLP-1 for Weight Loss

Additional Services You May Need
• Weight Loss Management
• Diabetes
• Hypertension
• Geriatric
• Personalized Care
• Primary Care
• Musculoskeletal Injuries
• Preventative Care
• Mental Health
• Heart Disease
• Congestive Heart Failure
• Same Day Sick Visits
• Physical Exams
• Chronic Care Management
• Wellness Visits
• Acute Care Visits
• Women’s Health
• Depression
• ADHD
• Asthma
• COPD
• Sleep Apnea
• Gastrointestinal Disorders
• Migraine
• Ailments and Procedures
• Internal Medicine
• Concierge Medicine
• Vitamin B12 Injections
• IV Hydration Therapy
• Auto Accident Injury
• Pre Operation Clearance Physicals
• Integrative Medical Weight Loss
• Oral GLP-1 for Weight Loss